Common Errors
Antivirus and Security Software
Turbo applications are compatible with all major antivirus and security software vendors. However, there are many configurations of these which can cause errors or hangs in Turbo applications. If encountering issues, a good first step is to disable any security software to rule it out as a possible cause.
Turbo Virtual Machine 0x0003
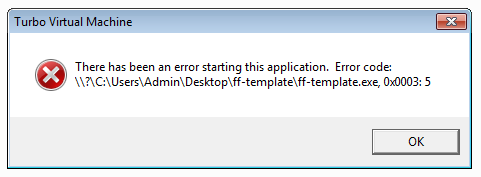
This error indicates that there is a problem accessing the container executable from itself. This can occur from security software that limits what applications have access to or if the application was started with a low privilege user which doesn't have access to the folder where the executable resides.
Try adding exclusions to your security software for the application. Also, try enabling the Launch child processes as user setting.
Unable to load a required virtual machine component
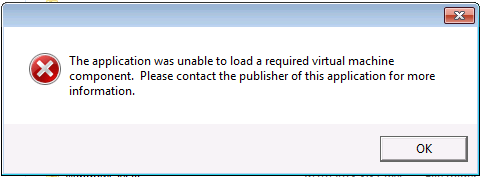
This error indicates that the container cannot access files in the environment found in the application directory. The most common reason for this is that the application path is not being resolved correctly. This can happen if there are path resolution rules defined for the container. For example, if there is a Snapshot Directory mapping from @PROGRAMFILES@ to c:\program files (x86), then running the container from c:\program files will fail. See xappl reference for more information.
Large Applications
If you attempt to execute an EXE file over 4GB in size you will get the error message:
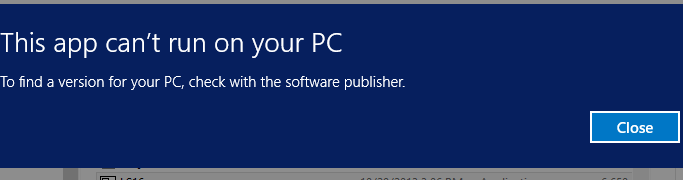
See the article on handling Large Applications for information on containerizing and optimizing large applications.
Command Line Errors
Applications cannot be run by anonymous users
Applications cannot be run by anonymous users.
Would you like to upgrade your account now? (y/n)
Ensure the correct domain is set and login to a valid Turbo Server account:
turbo config --domain=<your domain>
turbo login <username>
Sandbox is already in use
Critical error: An unhandled exception has occured
Please contact [email protected]
Sandbox is already in use.
There is an existing instance of the application that is in use. Use turbo stop <containerid> to stop the existing instance. If the command does not succeed, find the corresponding turbo.exe process using Task Manager and kill process. If the process cannot be found, use Process Explorer to find the process. You can find virtual processes by searching for the string handle _xvm_mtx.