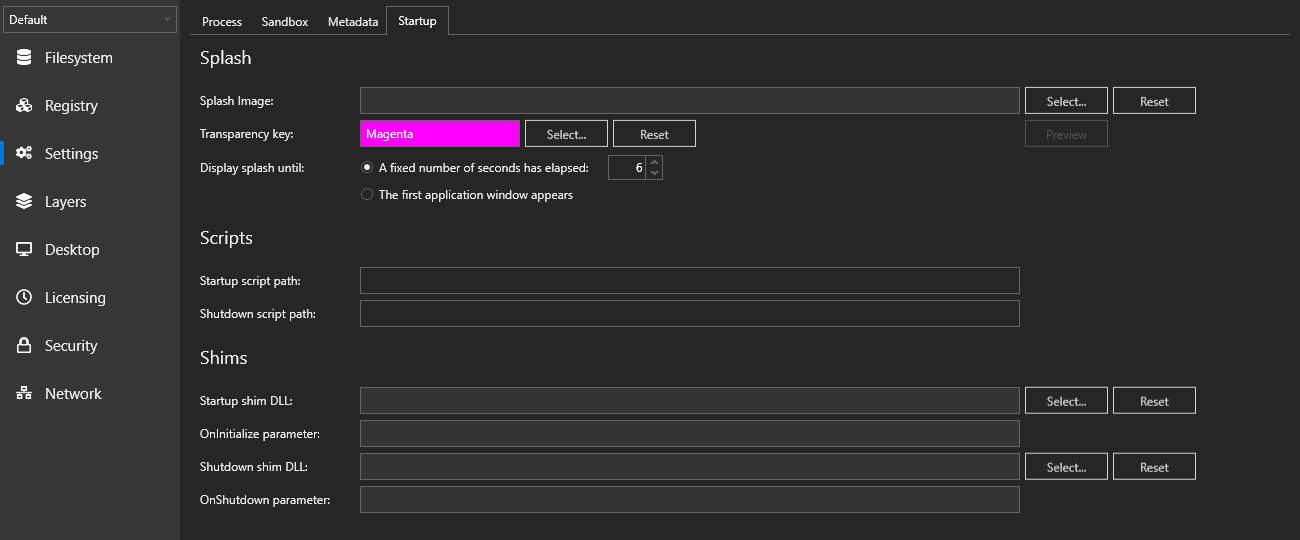
Startup/Shutdown Scripts and Shims
Turbo Studio allows for custom operations to be performed at the beginning and end of a container's life. This allows for application specific configuration steps to be performed before a container starts (ie. install a necessary driver) or clean up to be performed afterward.
Container Life Cycle
Containers are managed with a root parent process known as a "bootstrap process". This process hosts the virtual machine engine from which the rest of the container executes. In the Turbo command line environment, turbo.exe hosts a shared bootstrap process for each instance of the same container. For Turbo standalone executables ("ISV Applications"), a seperate bootsrap process is used for each invocation of the .exe.
Startup shims and scripts are executed when the first container bootstrap process is started but before the startup files are launched. Execution of the shims and scripts will block the startup files so any long running operations will delay container startup.
Shutdown shims and scripts are executed when the last process inside the container is closed.
Scripts
For simple tasks, a .bat or .cmd script can be configured.
Put the script in the container file system (a full isolated folder in @SYSDRIVE@ such as "scripts" is recommended). Specify the full path to the script in studio. Note that the untokenized form of the path must be used here (c:\scripts\init.cmd rather than @SYSDRIVE@\scripts\init.cmd). Environment variables can also be used in the path (ex: %systemdrive%\scripts\init.cmd) if they are defined on the machine or in the container's custom environment variables.
An example startup script might look like this:
@ECHO Initializing environment
if exist C:\workspace\first goto Skip
:Create-Workspace
@ECHO Preparing Workspace
mkdir C:\workspace\first
echo print("Hello World!") > C:\workspace\first\helloworld.py
goto Done
:Skip
@ECHO Workspace already created, skipping step
:Done
@ECHO Done.
exit
A common use of startup scripts is to install some required component (driver, etc) to the native system if not already present. Such installers will require admin privileges so will require UAC elevation. Below is one way this can be accomplished using a runtime generated VBS script:
# create vbs script to ShellExecute a command with "runas" verb to show the UAC prompt if required
echo Set UAC = CreateObject^("Shell.Application"^) > "%temp%\elevate.vbs"
echo UAC.ShellExecute "cmd.exe", "/c ""c:\path\to\installer.exe", "", "runas", 1 >> "%temp%\elevate.vbs"
# execute the vbs script and wait until it completes
start /b /wait >nul cscript /nologo "%temp%\elevate.vbs" 2>&1
# clean up
del "%temp%\elevate.vbs"
To troubleshoot script issues, set the __DEBUGINITSCRIPTSHIM environment variable to true. This will show the command window that is executing the script so you can see output and any generated errors.
Shims
For complex tasks, a DLL can be written to be executed. DLLs can be written in any programming language that supports them but do note any framework requirements must be configured inside the container.
The shim must conform to Turbo Studio interface in order to be loaded properly. Startup shims must be compiled with an exported OnInitialize function. Shutdown shims must be compiled with an exported OnShutdown function. The same DLL can be used for both if both functions are exported.
Shim function signatures:
typedef BOOL (__stdcall *FnOnInitialize) (LPCWSTR pwcsInitializationToken);
typedef void (__stdcall *FnOnShutdown)(LPCWSTR pwcsShutdownToken);
The return value of the startup shim indicates to the bootstrap process whether it should proceed with execution of the container.
The functions are acquired by the virtual machine with LoadLibrary and GetProcAddress win32 APIs.
LPCWSTR pwcsInitToken = "VendorSpecificToken";
HMODULE hShim = ::LoadLibrary("c:\path\to\shim.dll");
FnOnInitialize fnOnInit = (FnOnInitialize)::GetProcAddress(hShim, "OnInitialize");
BOOL fResult = fnOnInit(pwcsInitToken);
Note that the DLL must be compiled for the correct architecture (x86 or x64) in order to be loaded. Since the DLL is loaded by the bootstrap process, it must match its architecture, not the startup file.